Total Solution to Earthing & Lightning Protection |
9AKK106354A3360
16/11
16
The mesh method
IEC/BS EN 62305 lists four different air termination mesh
sizes that are defined and correspond to the relevant class
of LPS (see Table 9).
This method is suitable where plain surfaces require
protection if the following conditions are met:
–– Air termination conductors must be positioned at roof
edges, on roof overhangs and on the ridges of roof with a
pitch in excess of 1 in 10 (5.7º)
–– No metal installation protrudes above the air
termination system
Modern research on lightning inflicted damage has shown
that the edges and corners of roofs are most susceptible to
damage. So on all structures particularly with flat roofs,
perimeter conductors should be installed as close to the
outer edges of the roof as is practicable.
The IEC/BS EN 62305 Standard permits the use of
conductors (whether they be fortuitous metalwork or
dedicated LP conductors) under the roof. Vertical air rods
(finials) or strike plates should be mounted above the roof and
connected to the conductor system beneath.
The air rods should be spaced not more than 10 m apart
and if strike plates are used as an alternative, these
should be strategically placed over the roof area not more
than 5 m apart.
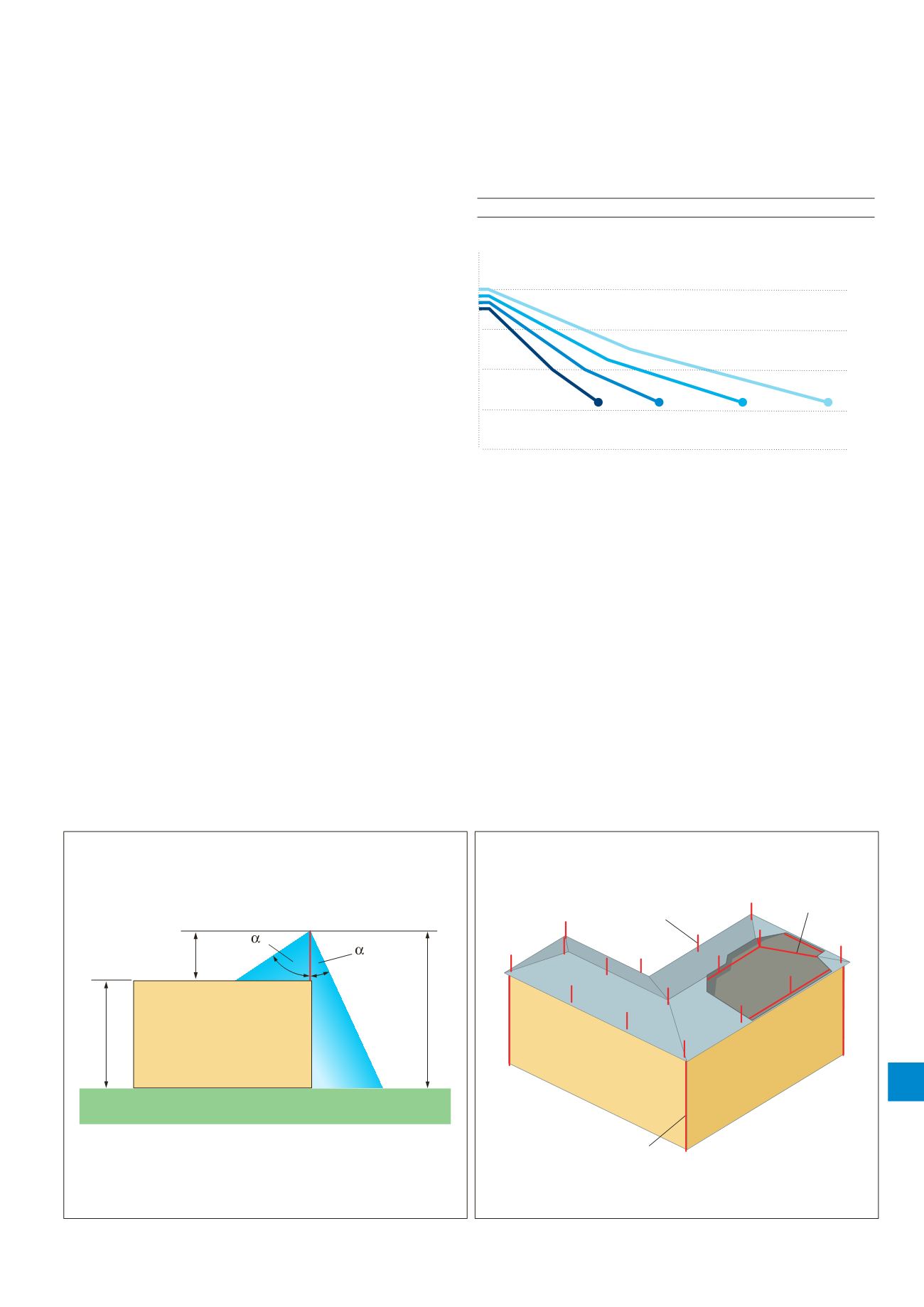
Figure 10. Concealed air termination network
Figure 8. Effect of the height of the
reference plane on the protection angle
FIgure.9
Determination of the protective angle (IEC/BS EN 62305-3 Table 2)
α
°
80
60
40
20
0
2 10 20 30 40 50 60
h
(m)
Class of LPS
I
II
III
IV
Note 1:
Not applicable beyond the values marked with
l
Only rolling sphere and mesh methods apply in these cases
Note 2:
h
is the height of air-termination above the reference plane of the area
to be protected
Note 3:
The angle will not change for values of
h
below 2m
h
h
2
h
1
2
1
Concealed
conductor
Vertical air
termination
or strike plate
Ho izo tal
conductor
Vertical air
termination
Cross section of roof ridge
Roof pitch
Down conductor