TSC-0912 - 09.10.12
Furse, Wilford Road, Nottingham, NG2 1EB • Tel: +44 (0)115 964 3700 • Email:
enquiry@furse.com• Web:
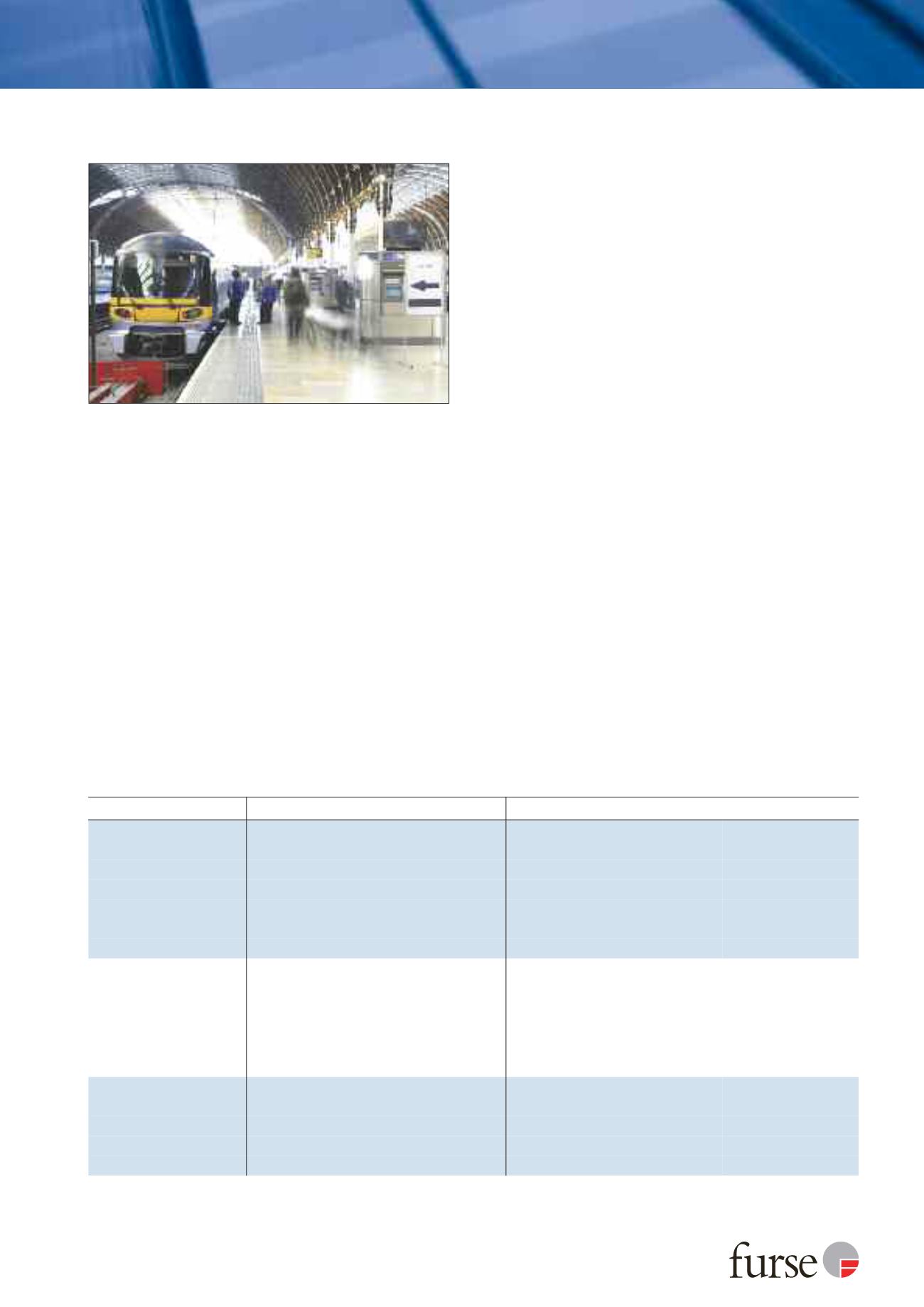
www.furse.comProtecting rail networks
Safety, reliability and availability of service are
essential prerequisites for a rail network.
For all types of network, from mass transit systems and
mainline services to metros, airport links and light rail,
this has clear implications for the sensitive and critical
electronic systems installed throughout.
These systems manage network performance, and
ensure its continuous safe and practical operation. Yet
they can easily be damaged or degraded by transient
overvoltages, caused by:
Partial lightning currents entering an electrical
system following a direct lightning strike to a
network location
Indirect lightning (nearby lightning strikes) to the
rail network, leading to transient overvoltages
entering an electrical system via a local earthing
arrangement (resistive coupling), or via overhead
metallic service lines (inductive coupling)
Outright damage to electronic systems causes service
interruptions and network downtime leading to
customer dissatisfaction and maintenance costs.
Degradation leads to reduced equipment reliability
and lower equipment lifetimes, risking sudden,
unpredictable or intermittent failures.
Installing protection against transient overvoltages
throughout the network is therefore critical.
Transient overvoltage protection should be applied on
(but not limited to):
Power supplies throughout the network, including
trackside cabinets, level crossings and at stations
and terminals
Signalling networks including trackside Solid State
Interlocking (SSI) systems
Telecommunications equipment and trackside
telephones
CCTV monitoring systems
Passenger information systems, ticketing and
gating operations
Security systems and critical safety equipment such
as fire detection and fire alarm systems
Effective, repeat protection against transient
overvoltages can be achieved through installation of
Furse Surge Protective Devices as part of an overall
Lightning Protection System to BS EN/IEC 62305.
Key protection locations together with the appropriate
Furse SPD are shown in the table below.
Many of these SPDs have Network Rail approval (see
individual product pages for further reference).
Transient overvoltage protection for rail networks
Location
Requirement
Protection measure (SPD)
Main terminals & stations
Protect 3-phase & 1-phase power supplies
ESP M1 Series
See page 192
ESP D1 Series
See pages 186 & 188
ESP M2/M4 Series
See page 190
ESP 415/XXX Series
See page 184
Protect critical systems (e.g. fire fighting equipment)
ESP 5A/BX & ESP 16A/BX Series
See page 198
Protect telecoms systems
ESP D, E, H Series
See pages 204-209
ESP SL Series
See page 212
Trackside location
Protect trackside signalling equipment (SSI systems)
ESP SSI/M & ESP SSI/B
See page 252
Cabinets (LOCS)
& radio network
ESP RF Series
See pages 258-261
Protect power supplies
SSI/120AC & ESP SSI/140AC
See page 252
ESP M1 Series
See page 192
ESP D1 Series
See pages 186 & 188
Maintain TFMs/SSI datalinks
ESP PTE002 Tester
See page 266
Level crossings
Protect CCTV systems
ESP 5A/BX & ESP 16A/BX Series
See page 198
ESP CCTV Series
See page 256
ESP D Series
See page 204
Signalling equipment & radio network
ESP SSI Series
See page 252
ESP RF Series
See pages 258-261
Note: list of Surge Protection Measures shown above is not exhaustive. Additional electronic systems may require transient overvoltage protection on a case-by-case
basis. Please contact us to discuss particular project requirements.