A-36
Functions and
characteristics
Motor protection
General information on motor feeders
The parameters to be considered for motor-
feeder protection depend on:
b
the application (type of machine driven,
operating safety, frequency of operation,
etc.)
b
the level of continuity of service required
by the load or the application
b
the applicable standards for the protection
of life and property.
The required electrical functions are:
b
isolation
b
switching, generally at high endurance
levels
b
protection against overloads and short-
circuits, adapted to the motor
b
additional special protection.
Amotor feeder must comply with the
requirements of standard IEC 60947-4-1
concerning contactors and their protection:
b
coordination of feeder components
b
thermal-relay trip classes
b
contactor utilisation categories
b
coordination of insulation.
Motor-feeder function
Amotor feeder comprises a set of devices for motor protection and control, as well
as for protection of the feeder itself.
Isolation
The purpose is to isolate the live conductors from the upstream distribution system to
enable work by maintenance personnel on the motor feeder at no risk. This function
is provided by a motor circuit breaker offering positive contact indication and lockout/
tagout possibilities.
Switching
The purpose is to control the motor (ON / OFF), either manually, automatically or
remotely, taking into account overloads upon start-up and the long service life
required. This function is provided by a contactor. When the coil of the contactor's
electromagnet is energised, the contactor closes and establishes, through the poles,
the circuit between the upstream supply and the motor, via the circuit breaker.
Basic protection
Short-circuit protection
b
Detection and breaking, as quickly as possible, of high short-circuit currents to avoid
damage to the installation. This function is provided by a magnetic or thermal-
magnetic circuit breaker.
Overload protection
b
Detection of overload currents and motor shutdown before temperature rise in the
motor and conductors damages insulation. This function is provided by a thermal-
magnetic circuit breaker or a separate thermal relay.
Overloads: I < 10 x In
They are caused by:
b
an electrical problem, related to an anomaly in the distribution system (e.g. phase failure,
voltage outside tolerances, etc.)
b
a mechanical problem, related to a process malfunction (e.g. excessive torque) or damage to
the motor (e.g. bearing vibrations).
These two causes will also result in excessively long starting times.
Impedant short-circuits: 10 x In < I < 50 x In
This type of short-circuit is generally due to deteriorated insulation of motor windings or
damaged supply cables.
Short-circuits: I > 50 x In
This relatively rare type of fault may be caused by a connection error during maintenance.
Additional electronic protection
Locked rotor
b
Under-load
b
Long starts and stalled rotor
b
Insulation faults.
b
Motor-feeder solutions
6WDQGDUG ,(& GH¿QHV WKUHH W\SHV RI GHYLFH FRPELQDWLRQV IRU WKH SURWHFWLRQ RI
motor feeders.
Three devices
magnetic circuit breaker + contactor + thermal relay.
b
Two devices
thermal-magnetic circuit breaker + contactor.
b
One device
thermal-magnetic circuit breaker + contactor in an integrated solution (e.g.
b
Tesys U).
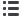
DB115571
M
Isol
a
tion
a
nd short-circuit protection
Circuit bre
ak
er
w
ith
mag
netic protection
Cont
a
ctor
A
ddition
a
l protection
f
unctions
Po
w
er s
w
itchin
g
Ther
ma
l protection,
sep
a
r
a
te or built into
the circuit bre
ak
er
Overlo
a
d protection
or ther
ma
l protection
S
peci
f
ic or intern
a
l
m
otor protection
Switchgear functions in a motor feeder.
Phase unbalance or phase loss protection
b
Phase unbalance or phase loss can cause temperature rise and braking torques that
can lead to premature ageing of the motor. These effects are even greater during
starting, therefore protection must be virtually immediate.
559E1500.indd
version: 1.0