TSC-0912 - 09.10.12
Furse, Wilford Road, Nottingham, NG2 1EB • Tel: +44 (0)115 964 3700 • Email:
enquiry@furse.com• Web:
www.furse.comAir termination
Protects rooftop mounted equipment from direct
lightning strikes
Complies with BS EN/IEC 62305 standard
Lightweight construction
Corrosion resistant
Quick and easy to assemble
Available in a range of heights from
0.5 m to 10 m
Range of frames and concrete weights for
different wind zones
Large protection zones
Modular, versatile and robust
Features & benefits
Interception air rod
(3 m to 4 m height)
2 piece interception
pole with square
support frame
4 square concrete
bases (or 8 double-
stacked for higher
wind speeds)
Interception air rod
(4.5 m to 5.5 m height)
2 piece interception
pole with tripod
support frame
3 circular
concrete bases
Interception air rod
(6 m to 8 m height)
3 piece interception pole
with tripod support frame
6 circular concrete bases
Interception air rod
(8 m to 10 m height)
3 piece interception pole with
‘H’ shaped support frame
10 circular concrete bases
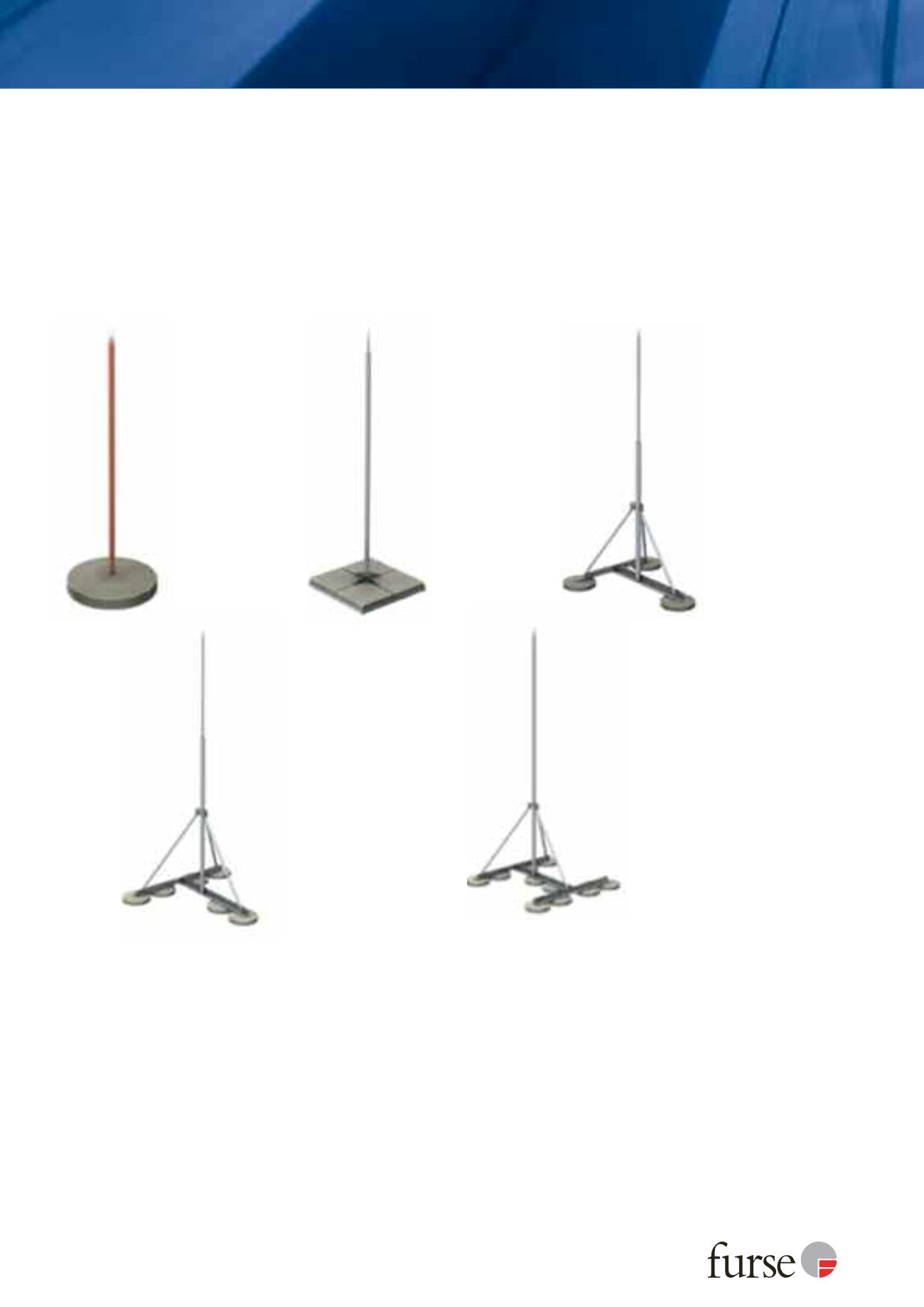
Interception air rod
(0.5 m to 2 m height)
Copper or aluminium
air rod
Circular concrete base
Rod connects directly
into base
Free standing air termination
Furse free standing interception air rods are designed to protect rooftop mounted or exposed equipment,
such as air conditioning units or photovoltaic panels, from a direct lightning strike.
Free standing interception air rods are easily constructed from a small range of components including air rod or
interception pole, support frame and concrete base, to create a complete unit which when connected to the air
termination network provides a highly versatile and effective lightning protection solution.
Note: installed interception air rods must have sufficient height to provide a clear zone of protection around the
equipment to be protected, as defined by BS EN/IEC 62305-3 (see protective angle method). Further information
can be found in the Furse Guide to BS EN 62305.