
5/28
Presentation, functions
The standardization of Web services has come about as a result of joint
development between Microsoft and IBM, amongst others, validated at the W3C
(
World Wide Web Consortium)
as an open “standard”.
It now provides all the tools, specifications and environments needed for each
platform. Web services are based on standards such as:
b
XML
(
eXtensible Markup Language)
:
the universal standard for data exchange
b
SOAP
(
Single Object Access Protocol)
protocol carried via the HTTP
(
Hyper Text
Transfer Protocol)
channel
b
WSDL
(
Web Services Description Language)
in XML format
SOAP is currently considered to be the reference protocol, including in industry. It
has now been adopted by the main market players, including Microsoft (
p
NET, SQL
Server, OFFICE, etc.), IBM (Java, Web Sphere), Lotus, ORACLE, SUN, SAP, etc.
Embedded SOAP/XML Web services: ModbusXMLDa Web services
This new Transparent Ready service offers the hitherto unheard of possibility of
making an IT/e-business application interact directly with the control system levels
using the same standards.
With the implementation of ModbusXMLDa
(
Modbus XML Data access)
services in
FactoryCast Web servers, IT engineers can easily create their own application to
access the required information directly in the PLC and in real time.
Data exchanges are made in XML standard format in response to a request using
the SOAP protocol.
The implementation of Web services in control system equipment makes it easy to
achieve vertical integration of the control level and create even more collaborative
architectures which can be used to link production systems to enterprise
management systems. It simplifies access to information,
reduces training, development and roll-out costs and increases productivity.
ModbusXMLDa Web services in FactoryCast modules
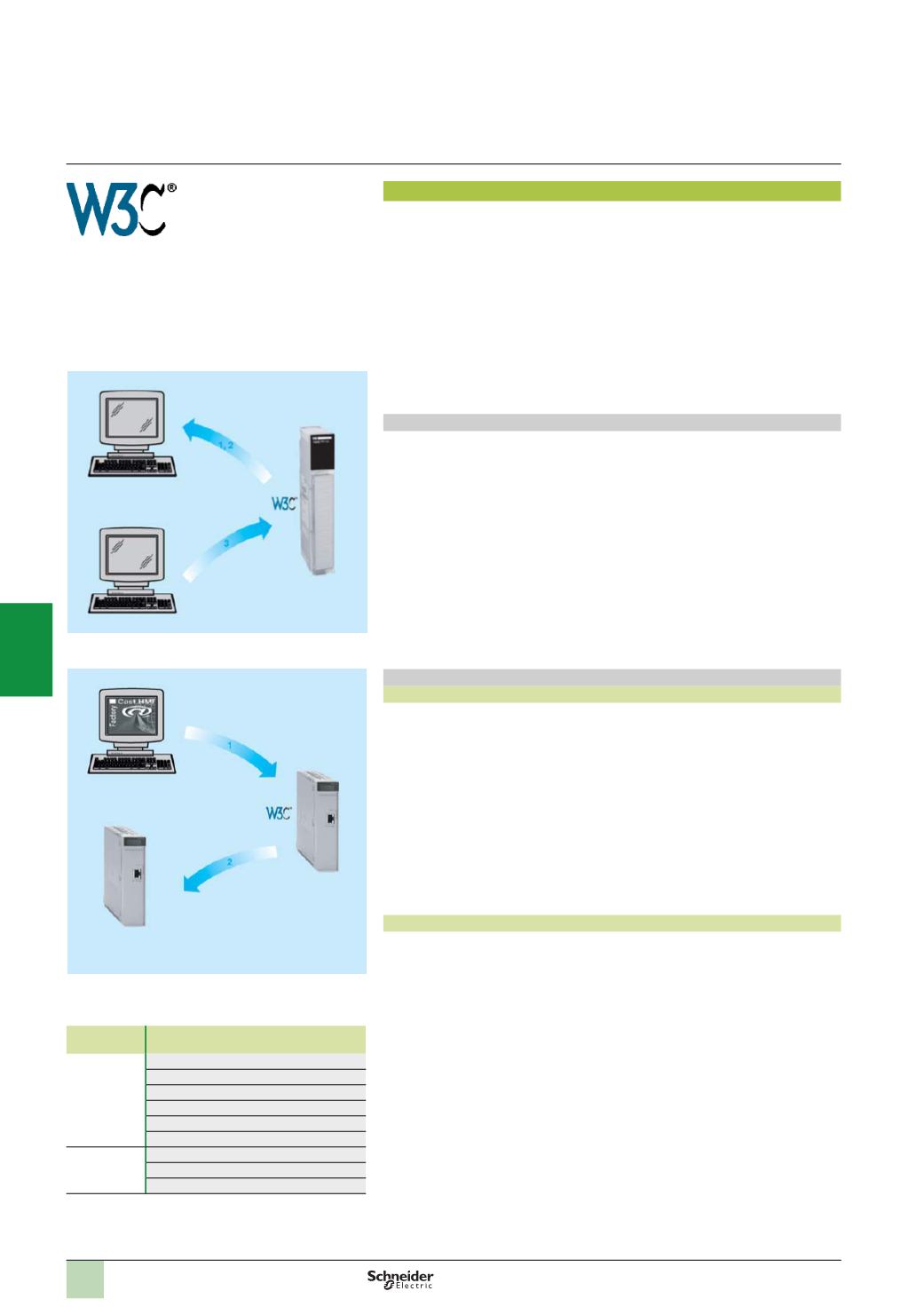
ModbusXMLDa server interface
This implementation enables a SOAP client application (management level
computer application, MES, ERP, etc.) to communicate directly with a FactoryCast
Web server module embedded in the PLC.
Exchanges are initiated by the SOAP client application (the server responds to these
requests).
b
Step 1: Creation of the client application with learning of the Web services. The
development environment (for example, Visual Studio
p
NET) looks in the
FactoryCast server for the list of available services and their WSDL standard
interfaces provided by the module.
b
Step 2: Development of the client application. The developer integrates the Web
service functions using the code retrieved at step 1 of the learning process.
b
Step 3: Execution of the client application. The client application communicates in
real time with the FactoryCast Web server module using the SOAP protocol.
ModbusXMLDa client interface
This implementation allows a FactoryCast HMI module to execute a SOAP client
application in order to communicate with a remote SOAP server application (for
example another FactoryCast Web server module or a computer management
application, MES, ERP, etc.).
Exchanges are initiated by the FactoryCast HMI client module (the remote
application server responds to SOAP requests sent by the FactoryCast HMI
module).
b
Step 1: Configuration of the ModbusXMLDa client service. The user declares the
PLC variables that are to be exchanged (in read or write mode), using the
FactoryCast HMI configuration software.
b
Step 2: Use of the application. The ModbusXMLDa client service executed in the
FactoryCast HMI module communicates directly with the remote server application
using SOAP requests in XML format.
Note
:
ModbusXMLDa functions are implemented in the FactoryCast modules:
-
Server interface: Modicon M340
BMX NOE 0110
,
Modicon Premium
TSX ETY 5103/WMY 100
and Modicon Quantum
140
NOE 771 11/NWM 100 00
-
Client interface: Modicon Premium
TSX WMY 100
and Modicon Quantum
140
NWM 100 00
SOAP
request
WSDL
Visual Studio
p
NET
p
NET Java
FactoryCast
module
SOAP
server
Development tool
SOAP
request
Configuration
SOAP
server
FactoryCast
HMI module
FactoryCast HMI software
SOAP
client
FactoryCast or
FactoryCast HMI
module
Requests
implemented
ModbusXMLDa functions implemented in
FactoryCast modules
Access to data
via physical
addresses
ReadDeviceIdentification
ReadMultipleRegisters
WriteMultipleRegisters
ReadCoils
WriteMultipleCoils
ReadDiscreteInputs
Access to data
via symbols
Read, operation to read item list value
Write, operation to write item list value
Browse, operation to browse item list
ModbusXMLDa server interface
ModbusXMLDa client interface
Presentation,
functions
Modicon Premium automation
platform
0
Ethernet Modbus/TCP network
SOAP/XMLWeb services
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10



















