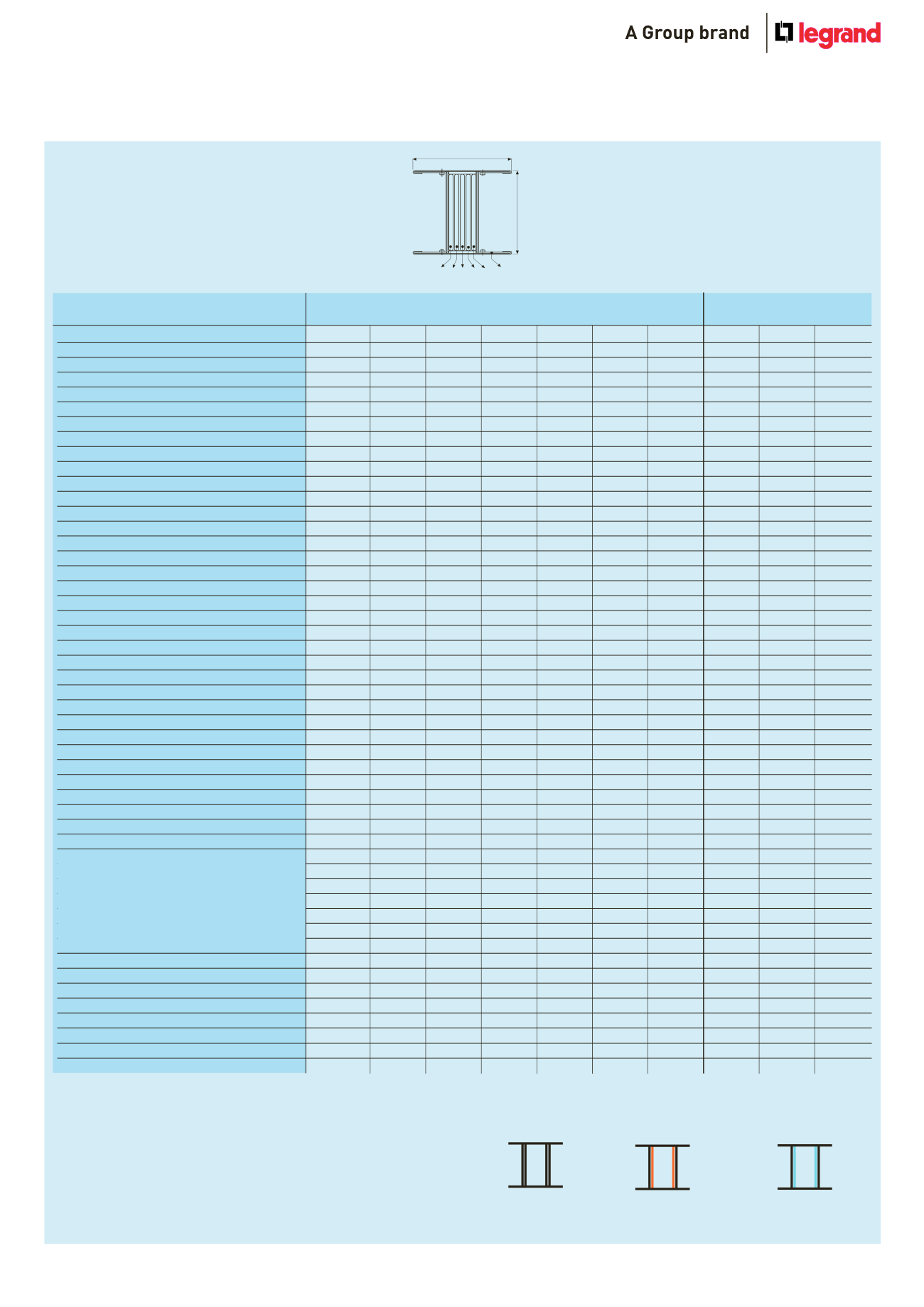
115
n
SCP technical data functional earth
clean earth / low noise SCP5C (3L + N + PE + FE)
copper
Rated current
I
n
[A]
800
1000
1250
1600
2000
2500
3200
4000
5000
Casing overall dimensions
L x H [mm] 140x130 140x130 140x130 140x170 140x170 140x220 140x380 140x440 140x480
Operating voltage
U
e
[V]
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
Insulation voltage
U
i
[V]
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
1000
Frequency
f [Hz]
50/60
50/60
50/60
50/60
50/60
50/60
50/60
50/60
50/60
Rated short-time current for three-phase fault (1 s) I
cw
[kA]rms
45
50
60
85
88
88
170
176
176
Allowable peak current for three-phase fault
I
pk
[kA]
95
110
132
187
194
194
374
387
387
Rated short-time current for single-phase fault (1 s) I
cw
[kA]rms
27
30
36
51
53
53
102
106
106
Allowable peak current for single-phase fault
I
pk
[kA]
57
66
79
112
116
116
224
232
232
Allowable specific energy for three-phase fault
I
2
t [MA
2
s]
2025
2500
3600
7225
7744
7744
28900
30976
30976
Phase resistance
R
20
[m
Ω
/m] 0·041
0·032
0·032
0·024
0·020
0·016
0·012
0·010
0·008
Phase reactance (50 Hz)
X [m
Ω
/m]
0·023
0·017
0·017
0·015
0·014
0·011
0·007
0·006
0·006
Phase impedance
Z [m
Ω
/m]
0·047
0·037
0·037
0·028
0·024
0·019
0·014
0·012
0·010
Phase resistance at thermal conditions
R
t
[m
Ω
/m] 0·045
0·037
0·040
0·029
0·024
0·019
0·015
0·013
0·010
Phase impedance at thermal conditions
Z [m
Ω
/m]
0·023
0·017
0·017
0·015
0·014
0·011
0·007
0·006
0·006
Neutral resistance
R
20
[m
Ω
/m] 0·041
0·032
0·032
0·024
0·020
0·016
0·012
0·010
0·008
Functional earthing resistance (FE)
R
20
[m
Ω
/m] 0·041
0·032
0·032
0·024
0·020
0·016
0·012
0·010
0·008
Functional earthing reactance (FE)
X [m
Ω
/m]
0·023
0·017
0·017
0·015
0·014
0·011
0·007
0·006
0·006
Resistance of the protective conductor (PE type 1) R
PE
[m
Ω
/m] 0·125
0·125
0·125
0·113
0·113
0·101
0·075
0·069
0·065
Resistance of the protective conductor (PE type 2) R
PE
[m
Ω
/m] 0·036
0·036
0·036
0·028
0·028
0·023
0·014
0·012
0·011
Resistance of the protective conductor (PE type 3) R
PE
[m
Ω
/m] 0·050
0·050
0·050
0·041
0·041
0·033
0·021
0·018
0·017
Reactance of the protective conductor (50 Hz)
X
PE
[m
Ω
/m] 0·054
0·054
0·054
0·044
0·044
0·032
0·022
0·017
0·016
Resistance of the fault loop (PE 1)
R
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·076
0·063
0·065
0·049
0·042
0·033
0·025
0·022
0·017
Resistance of the fault loop (PE 2)
R
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·064
0·054
0·057
0·042
0·036
0·029
0·021
0·018
0·015
Resistance of the fault loop (PE 3)
R
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·067
0·057
0·059
0·045
0·038
0·030
0·023
0·020
0·015
Reactance of the fault loop (50 Hz)
X
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·077
0·071
0·071
0·059
0·058
0·043
0·029
0·023
0·022
Impedance of the fault loop (PE 1)
Z
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·108
0·095
0·097
0·077
0·071
0·054
0·039
0·032
0·028
Impedance of the fault loop (PE 2)
Z
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·100
0·089
0·091
0·073
0·068
0·052
0·036
0·030
0·026
Impedance of the fault loop (PE 3)
Z
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·102
0·091
0·093
0·074
0·069
0·052
0·037
0·030
0·027
Zero-sequence resistance phase - N
R
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·170
0·155
0·155
0·115
0·120
0·098
0·083
0·071
0·062
Zero-sequence reactance phase - N
X
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·159
0·151
0·151
0·114
0·098
0·065
0·056
0·055
0·042
Zero-sequence Impedance phase - N
Z
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·233
0·216
0·216
0·162
0·155
0·118
0·100
0·090
0·075
Zero-sequence resistance phase - PE
R
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·408
0·320
0·320
0·220
0·188
0·142
0·092
0·077
0·061
Zero-sequence reactance phase - PE
X
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·196
0·158
0·158
0·126
0·135
0·136
0·104
0·088
0·075
Zero-sequence Impedance phase - PE
Z
o
[m
Ω
/m] 0·453
0·357
0·357
0·254
0·231
0·197
0·139
0·117
0·097
cos
ϕ
= 0·70 41·3
33·0
34·6
27·1
23·5
18·5
13·2
11·5
9·8
cos
ϕ
= 0·75 42·1
33·8
35·5
27·7
23·9
18·8
13·5
11·8
9·9
cos
ϕ
= 0·80 42·8
34·5
36·3
28·1
24·2
19·1
13·8
12·1
10·0
cos
ϕ
= 0·85 43·3
35·0
37·0
28·4
24·4
19·2
14·0
12·2
10·1
cos
ϕ
= 0·90 43·4
35·3
37·3
28·5
24·4
19·2
14·1
12·3
10·1
cos
ϕ
= 0·95 42·9
35·1
37·2
28·2
23·9
18·8
14·0
12·2
9·8
cos
ϕ
= 1·00 38·6
32·1
34·4
25·4
21·2
16·7
12·7
11·2
8·7
Weight (PE 1)
p [kg/m]
34·7
39·2
39·2
50·1
57·4
72·7
94·8
112·0
140·1
Weight (PE 2)
p [kg/m]
37·8
42·3
42·3
54·3
61·6
78·1
103·0
121·7
150·7
Weight (PE 3)
p [kg/m]
35·7
40·2
40·2
51·5
58·8
74·5
97·5
115·2
143·5
Fire load
[kWh/m]
5·6
6·9
6·9
10·0
10·3
13·1
20·0
23·8
26·3
Degree of protection
IP
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
55
Thermal resistance class of the insulating materials
–
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
B/F
1
Joule effect losses at rated current
P [W/m]
86
111
186
225
294
361
451
619
750
Min./max. ambient temperature
[°C]
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
-5/50
Voltage drop factor with
distributed load
k [V/m/A]10
-6
∆
V = k.L.Ie.10
-6
[V]
Single bar
Copper
Double bar
Regulations and conformity :
IEC/EN 60439-1 and 2; DIN VDE 0660 500 and 502
Product suitable for Constant/Cyclic Warm, humid climates :
DIN IEC 68 part 2-3; DIN IEC 68 part 2-30
Degree of protection :
IP 55; IP x7 carrying lines available with accessories, on request - +44 (0) 845 600 6266
Insulation and surface treatment of the conductors :
Insulated conductors for the whole length, aluminum copper-plated and tin-plated
Busbar casing material :
1·5 mm galvanised steel plate, pre-painted or stainless steel
(available, if required, with special paint and/or with thickness 2 mm)
1 : Class F thermal resistance (155°C) available on request
-
+44 (0) 845 600 6266
In : rated current referred to a room temperature of 40°C
PE 1
Standard version
PE 2
Extra earth - copper
PE 3
Extra earth - aluminium
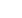
140
H
FE
PE
L2 L1N L3
SCP super compact busbar
– 5 conductor (copper)
technical data