1.69
Data is subject to errors and technical modifications.
Fuse Combination Units
Technical Data
Commercial
Distribution
Fuse - Combination Units - BS EN 60947-3
Many people are attracted to fuse-combination units by their
simplicity in application and their reliability in operation. They are particularly
useful for use on very high prospective fault level systems where the high
energy limiting characteristic of the HRC fuse can be effectively utilised.
In the past fuse-combination units came in two forms:
Switch Fuse
A switch in which one or more poles
have a fuse in series.
Fuse Switch
A switch in which one or more poles
have a fuse carrier/link which forms the
moving contact.
The definitions of these two basic types of fuse combination units have now
been extended to include units suitable for making,
breaking and isolation and units which are only suitable for providing isolation
for maintenance work.
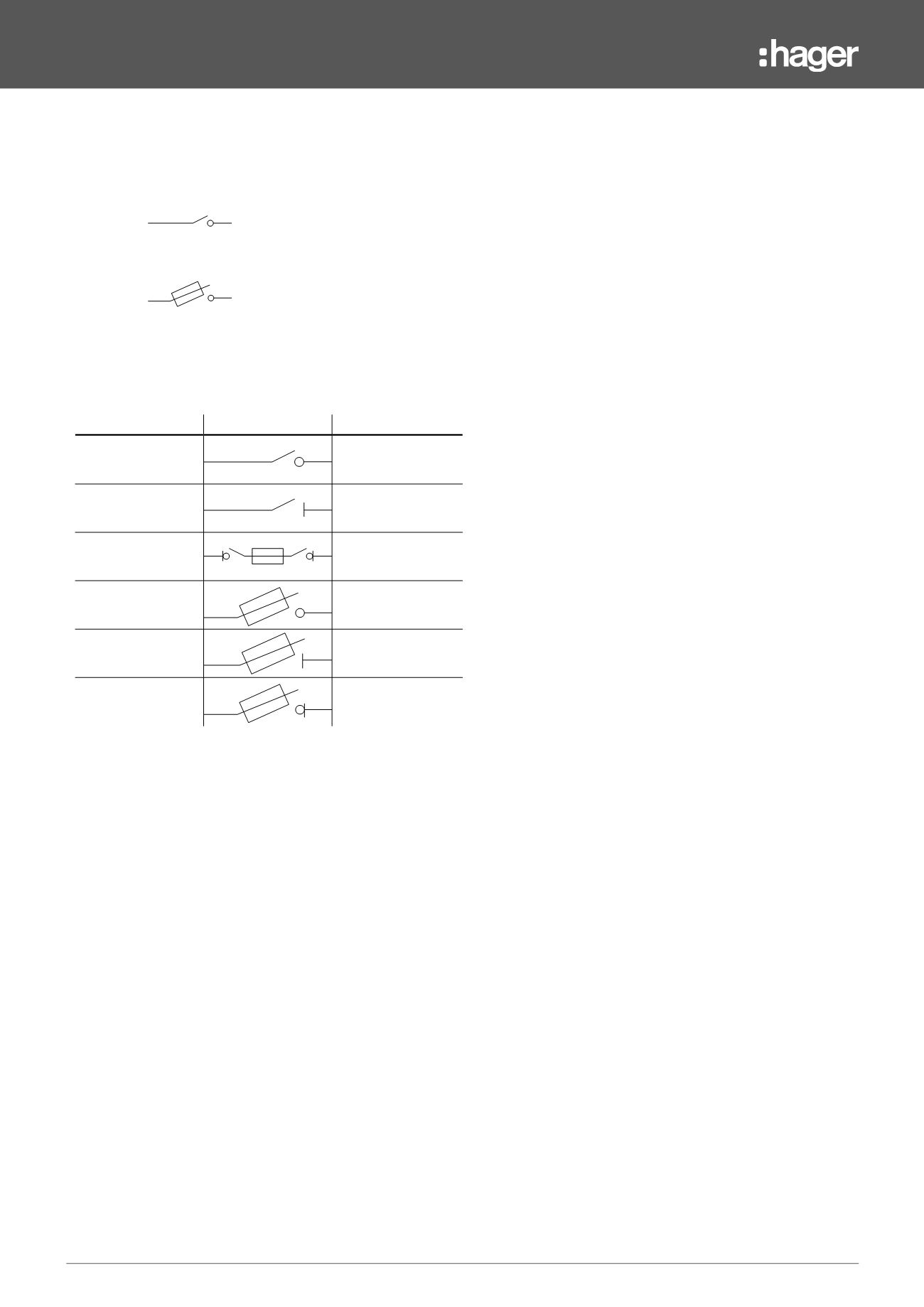
Definition
Symbol
Function
Switch Fuse
Making and
breaking current
Disconnector Fuse
Isolating
Switch Disconnector
Fuse
Making, breaking and
isolating
Fuse Switch
Making and
breaking current
Fuse Disconnector
Isolating
Fuse Switch
Disconnector
Making, breaking and
isolating
However, in order to keep the selection of fuse-combination units as simple as
possible, Hager offer a range of high performance double break switch-fuses,
which also satisfy the isolating requirement of the British standard. These are
correctly shown as and defined as a Fuse Combination Switch.
Switch disconnectors - BS EN 60947-3. A range of switch disconnectors
(isolators) are available for use on lower current ratings from 20A to 125A.
These switches are rated at AC-22 and provide a cost effective alternative to
the fuse combination switch, especially where the utilisation category AC-23
is not required. ie; mixed resistive and inductive loads.
Utilisation categories
Utilisation categories are not new but they are important because they help
the designer or specifier identify the correct unit for a particular application.
The designation of the utilisation category is made up of three parts:
1.
The prefix AC or DC, which indicates the nature of the current.
2.
The two digit number, which indicates the type of application
the unit is suitable for:
20 Connecting and disconnecting under no-load.
21 Switching of resistive loads.
22 Switching of mixed resistive and inductive loads.
23 Switching of highly inductive loads.
3.
The suffix A or B, which indicates whether the unit is suitable
for frequent or infrequent operation.
A Frequent operation
B Infrequent operation.
For example a fuse-combination unit feeding a 400V AC circuit of mixed
resistive and inductive loads which would need to be operated frequently
would require a minimum utilisation category of AC-22A.
If the load was highly inductive, i.e. motor loads, then the minimum utilisation
category would be AC-23A.
Generally, category AC-23 does not cover the switching of capacitors.
Usually this is the subject of agreement between manufacturer and user.
Motor Power Circuit Protection
Fuse-combination units can be used very effectively for motor power circuit
protection, the energy limiting HRC fuse offering very good protection to its
associated starter. Category AC-23A should be specified for this duty.
Special motor circuit protection fuse links are available which eliminate the
need to fit a larger bodied fuse just to take care of the starting current of the
motor.
The protection of motor power circuits should not be confused with the direct
switching of a single motor. If a fuse-combination unit is required to perform
this function then it must comply with the requirements of Appendix A of BS
EN 60947-3 which makes provision for different utilisation categories for this
application.