TECHNI CAL DATA
POWERSTAR
71
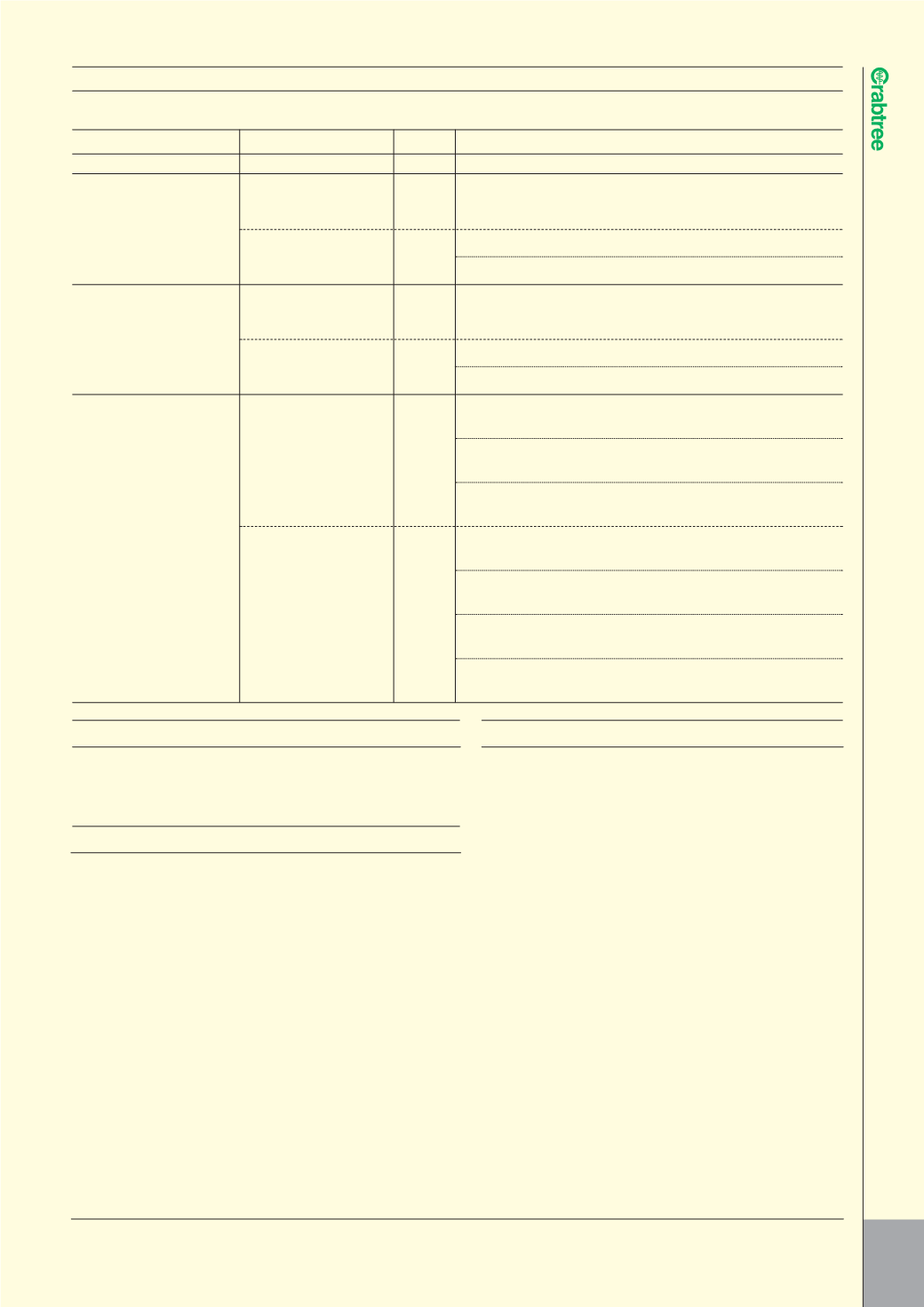
BSEN61439-1 : FORMS OF SEPARATION
l
FORMS OF SEPARATION
l
As described in BSEN60439-1 the Forms of Separation comprise four
levels as detailed in the above table. The various methods of achieving
separation can involve sleeving the busbars inside a separate box or a
combination of both methods.
COST EFFECTIVE SPECIFICATION
l
In order to gain maximum benefit from the standard it is necessary to
consider the application for which the switchboard is required and the
appropriate level of separation for the environment in which it is to be
installed. For example a Form 4 switchboard may be appropriate where
general access is permitted to the switch room but where the
switchboard is in a locked substation with access restricted to qualified
personnel, a lesser degree of separation may be more appropriate.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
l
Form 1 – No separation
Typical applications are places where the switchboard is in a secure
location and where failure of the switchboard will cause little or no
additional disruption to other areas being fed by the switchboard.
Form 2 – Separation of busbars from functional units.
Applications may well be the same as Form 1 but where it is
important that a fault in the switchboard need not affect all
functional units being fed from the same busbar system.
Form 3 – Separation of busbars from functional units and
the functional units from one another but not
their terminations.
Should be applied where it is important to provide protection from
internal live parts and where failure of functional units being fed
from the same busbar would cause unacceptable disruption.
Form 4 – Separation of busbars from functional units and
the functional units from one another including
their terminations.
Should be applied where it is important to provide protection from
internal live parts and where failure of functional units being fed
from the same busbar would cause unacceptable disruption.
Because all the terminations are separated it is possible to isolate
and work on a single functional unit.
- Separation of busbars from all
functional units
- Separation of all functional
units from one another
- Seperation of terminals for
external conductors associated
with a functional unit from the
terminals of any other
functionl unit and the busbars
- Seperation of the external
conductors from the busbars
- Seperation of the external
conductors associated with a
functional unit from other
functional units and their
terminals
- External conductors need not
be separated from each other
- Separation of busbars from all
functional units
- Separation of all functional
units from one another.
- Separation of terminals for
external conductors from the
functional units, but not from
the terminals of other
functional units.
Separation of busbars from all
functional units.
Terminals for external
conductors not separated
from busbars.
Terminals for external
conductors separated from
busbars.
Terminals for external
conductors in the same
compartment as the
associated functional unit.
Terminals for external
conductors not in the same
compartment as the
associated functional unit,
but in individual, separate,
enclosed protected spaces or
compartments.
Terminals for external
conductors not separated
from busbars.
Terminals for external
conductors and external
conductors separated from
busbars.
Form 2a
Form 2b
Form 3a
Form 3b
Form 4a
Form 4b
Type 7. All separation requirements are by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers
or partitions. The termination for each functional unit has its own
integral glanding facility
Type 6. All separation requirements are by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers
or partitions. Cables are glanded in common cabling chamber(s)
Type 5. Busbar separation is by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers or
partitions. Terminals may be separated by insulated coverings and
glanded in common cabling chamber(s)
Type 4. Busbar separation is achieved by insulated covering, e.g. sleeving,
wrapping or coatings. Cables may be glanded elsewhere
Type 3. Busbar separation is by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers or
partitions. The termination for each functional unit has its own integral
glanding facility
Type 2. Busbar separation is by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers or
partitions. Cables may be glanded elsewhere
Type 1. Busbar separation is achieved by insulated covering, e.g. sleeving,
wrapping or coatings. Cables may be glanded elsewhere
Form
Form 1
Type of Construction
Sub criteria
Main criteria
No separation
FORMS OF SEPARATION
Type 1. Busbar separation is achieved by insulated covering, e.g. sleeving,
wrapping or coatings.
Type 2. Busbar separation is by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers or
partitions
Type 1. Busbar separation is achieved by insulated covering, e.g. sleeving,
wrapping or coatings.
Type 2. Busbar separation is by metallic or non-metallic rigid barriers or
partitions