4. Spectrum
White sunlight is made up of electro-magnetic waves of
various lengths. Guiding a narrow beam of sunlight through
a glass prism displays a colour spectrum similar to the one
we see in a rainbow. During the generation of a rainbow the
numerous raindrops in the air act as prisms breaking up the
sunlight. Each colour represents a distinctive wavelength.
All light waves taken together create the impression of
white light
Coloured objects are perceived in their true colour only if
the respective colour is present in the spectrum of the light
source too. This is the case e.g. with the sun, incandescent
and luorescent lamps with good colour rendering qualities.
If the light of a low pressure sodium lamp e.g. is guided
through a glass prism though, only yellow radiation can be
perceived as the spectrum of this light source lacks all
colours except yellow.
5. Fading of materials
Fading of e.g. textiles is an efect of photo chemical
processes caused by the absorption of radiation energy.
The amount of change in colour depends on the intensity
of the illuminance the material is exposed to, the duration
of time the material is exposed to the radiation, the
temperature and the spectral formation of the radiation;
the shorter the wavelength the higher the energy of the
radiation. The fading efect can be slowed down by
reducing the illuminance, by switching on the light source
for short periods of time only, and by using light sources
emitting little shortwave radiation.
The fading risk can be calculated using the following formula:
FR = 0,02 x DF x E x t
FR = Fading risk
DF = Damage factor
E = Illuminance (lx)
t = Time (hrs)
A FR of 100 represents the exposure to light in a shop
window during summer with bright sunshine for one hour.
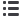
Spectral Luminosity
Wavelength
300 400 500 600
0,2
0,6
0,4
0,8
700
1,0
nm
Day
Night
Relative spectral luminosity
Sodium lamp
Fluorescent lamp
Light Source and Spectrum
Type of lighting
Damage factor
Daylight through 4 mm window glass 0,43 – 0,68
Incandescent lamps
0,08
Halogen lamps open
0,20
Halogen lamps with envelope or UV
block
0,12
SDW-T lamps
0,10
Metal halide lamps open
0,50
Metal halide lamps with envelope
0,2
Light colour luorescent lamps
/827
0,20
/830
0,20
/840
0,21
/865
0,26
/930
0,16
/940
0,18
/950
0,26
/33-640
0,27
Appendix>
Lighting Technology
Philips Lamps and Lighting Electronic Catalogue 2014
236
13