258
jcc.co.ukTechnical
Controlling lighting
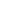
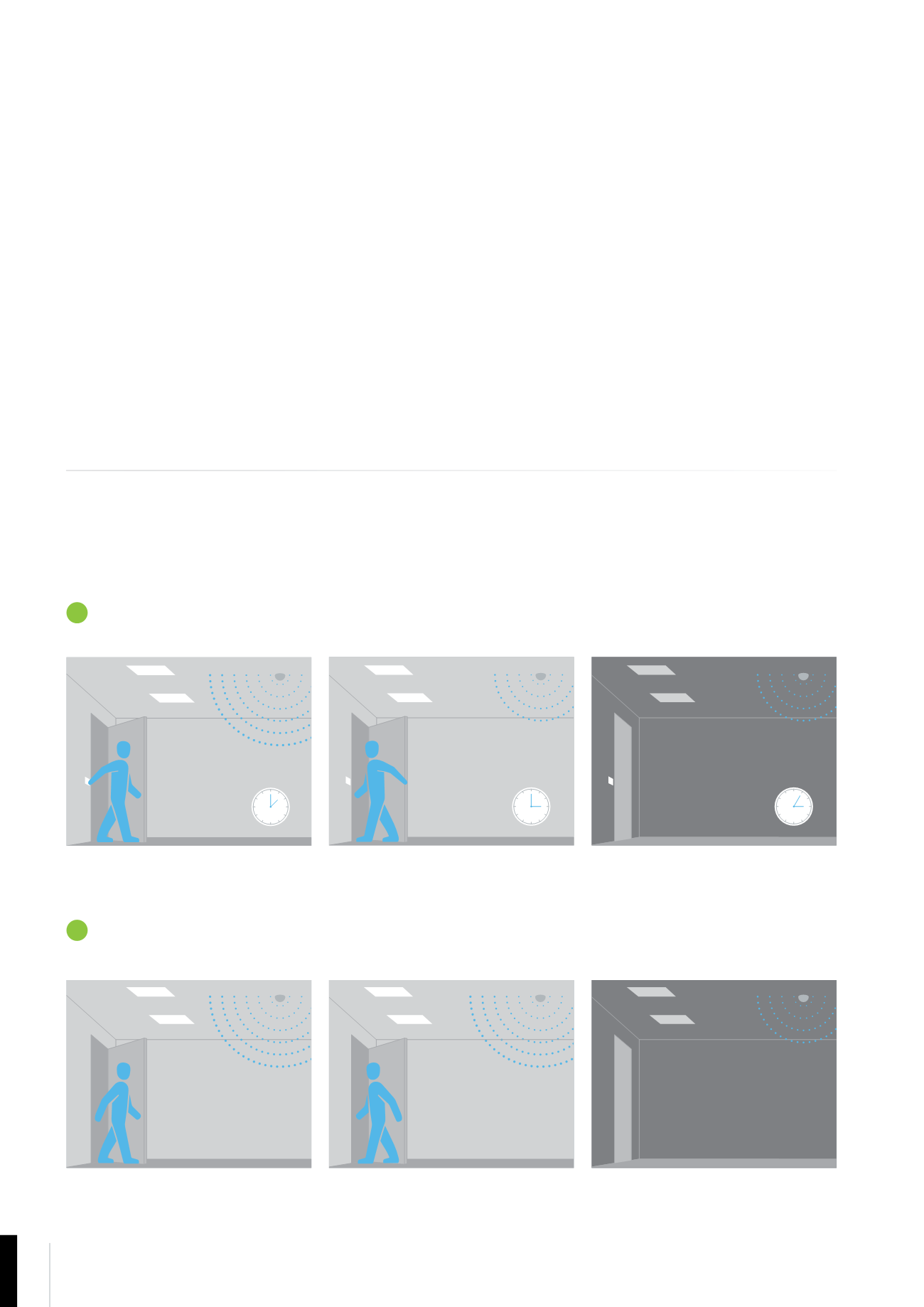
Lighting is switched on using a time switch
or detection from an occupancy sensor.
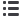
The lighting is switched on after detection
by an occupancy sensor.
The lighting stays on using a timer.
The sensor detects any further activity.
The lighting is automatically switched off
after a specified period of time.
The lighting is switched off when the
sensor doesn’t detect any further activity.
ABSENCE DETECTION
Manual on, auto off
PRESENCE DETECTION
Auto on, auto off
Why control lighting?
Switching to LED from traditional lighting technology, such as halogen or fluorescent, can provide up to 90% energy savings. However,
LED lighting can provide other benefits, such as instantly controlling on/off without deterioration in the fittings operating life. These
benefits are suitable for lighting control and allow for significantly improved energy savings and a better lit environment.
Lightingcontrols canprovideanadditional 50%energy saving
The government recognises the benefit of lighting control and is starting to introduce regulation that focuses on improvements in
the energy efficiency of a complete building. The introduction of Building Regulations Part L (2013) is an example of this change and
introduces the concept of a Lighting Energy Numeric Indicator (LENI – see page 256) that calculates the energy usage of a building
per metre
2
.
LENI
LENI is a new measurement of lighting that changes the focus from the performance of an individual fitting, to the performance of
the full lighting installation (see page 256).
What are the types of lighting control?
Good lighting control systems should adjust the lighting to compensate for changes in daylight levels and the usage of the area.
The main types of control are:
1
2