11
11/42
Dimensions
Section 12
Circuit breakers for direct
current applications (cont.)
24 V - 48 V direct current applications
Technical advice
DB124248
Continuity of service of the solutions
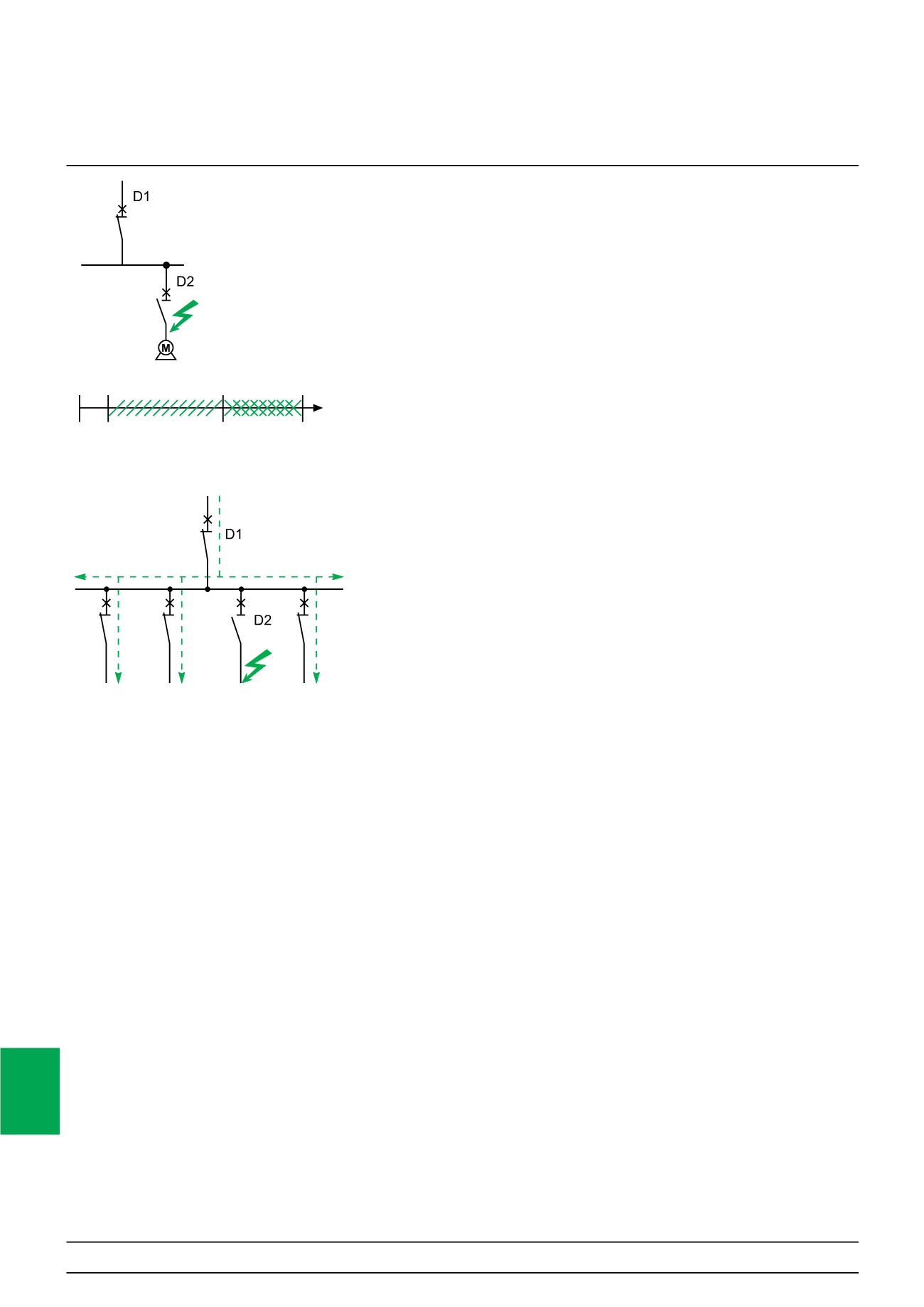
Discrimination of the direct current protection devices
Discrimination is a key element that must be taken into account right from the design
stage of a low-voltage installation to allow continuity of service of the electrical power.
Discrimination involves coordination between two circuit breakers connected in
series, so that in the event of a fault, only the circuit breaker positioned immediately
upstream of the fault trips. A discrimination current Is is defined as:
b
b
I fault < Is: only D2 removes the fault, discrimination ensured,
b
b
I fault > Is: both circuit breakers may trip, discrimination not ensured.
Discrimination may be partial or total, up to the breaking capacity of the downstream
circuit breaker. To ensure total discrimination, the characteristics of the upstream
device must be higher than those of the downstream one.
The same principles apply to designing both direct current and alternating current
installations. Only the limit currents change when direct current is used.
Once again, we find the same concepts of discrimination:
b
b
total
: up to the breaking capacity of the downstream device. Our tests have been
performed at up to 25 kA or 50 kA depending on the breaking capacity of the
devices in question.
b
b
partial
: indication of the discrimination limit current
Is
. Discrimination is ensured
below this value; above this value, the upstream device participates in the breaking
process,
b
b
none
: no discrimination ensured, the upstream and downstream circuit breakers
will trip.
For further information about the discrimination concept for protection devices in
general, refer to technical supplement 557E4300, "Discrimination of modular circuit
breakers".
Total discrimination solutions
In the following tables, we offer you solutions that favour continuity of service (total
discrimination between circuit breakers), for different short-circuit currents.
DB124247
Only D2 trips
D1 and
D2 trip
Ifault
0 D2
Is