63
MCBs - Technical
Data
GENERAL CONSTRUCTION
Wylex MCBs are of the thermal-magnetic current limiting type.
MCBs have an easy to operate handle with a trip-free toggle mechanism
– so even when the handle is held in the ‘on’ position the MCB is free
to trip.
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE CONSIDERATIONS
Wylex MCBs are calibrated to meet the requirements of BS EN 60898,
30°C Ref Calibration Temperature.
At other temperatures the following rating factors should be used:
At 60°C 0.9 At 20°C 1.0 At 0°C 1.1
Adjacent thermal-magnetic MCBs should not be continuously loaded at
or approaching their nominal rated currents when mounted in
enclosures. It is good engineering practice to apply generous derating
factors or make provision for adequate free air between devices.
In these situations, and in common with other manufacturers, we
recommend a 66% diversity factor is applied to the MCB nominal rated
current where it is intended to load the MCBs continuously (in excess
of 1 hour).
METHOD OF OPERATION
1 Moderate overload conditions
Detection of moderate overload conditions is achieved by the use of a
thermo-metal element which deflects in response to the current passing
through it.The thermo-metal element moves against the trip bar
releasing the trip mechanism.
2 Short circuit conditions
When the current flowing through the MCB reaches a predetermined
level, the solenoid directly pulls in the plunger which forcibly separates
the contacts and simultaneously releases the trip mechanism.
3 Establishment of arc between fixed and moving contacts
As the moving contact moves away from the fixed contact, an arc is
established.The arc runs along the arc runner to the arc chamber
where it is split up between the plates and extinguished.
The low inertia and consequent high speed of the moving contact has a
limiting effect on the flow of fault current.The rapid development of the
arc, together with its accelerated extinction in the arc chamber,
BS EN 60898-2 gives a typical operating time of 3.5-5 milliseconds for
a type B curve MCB.
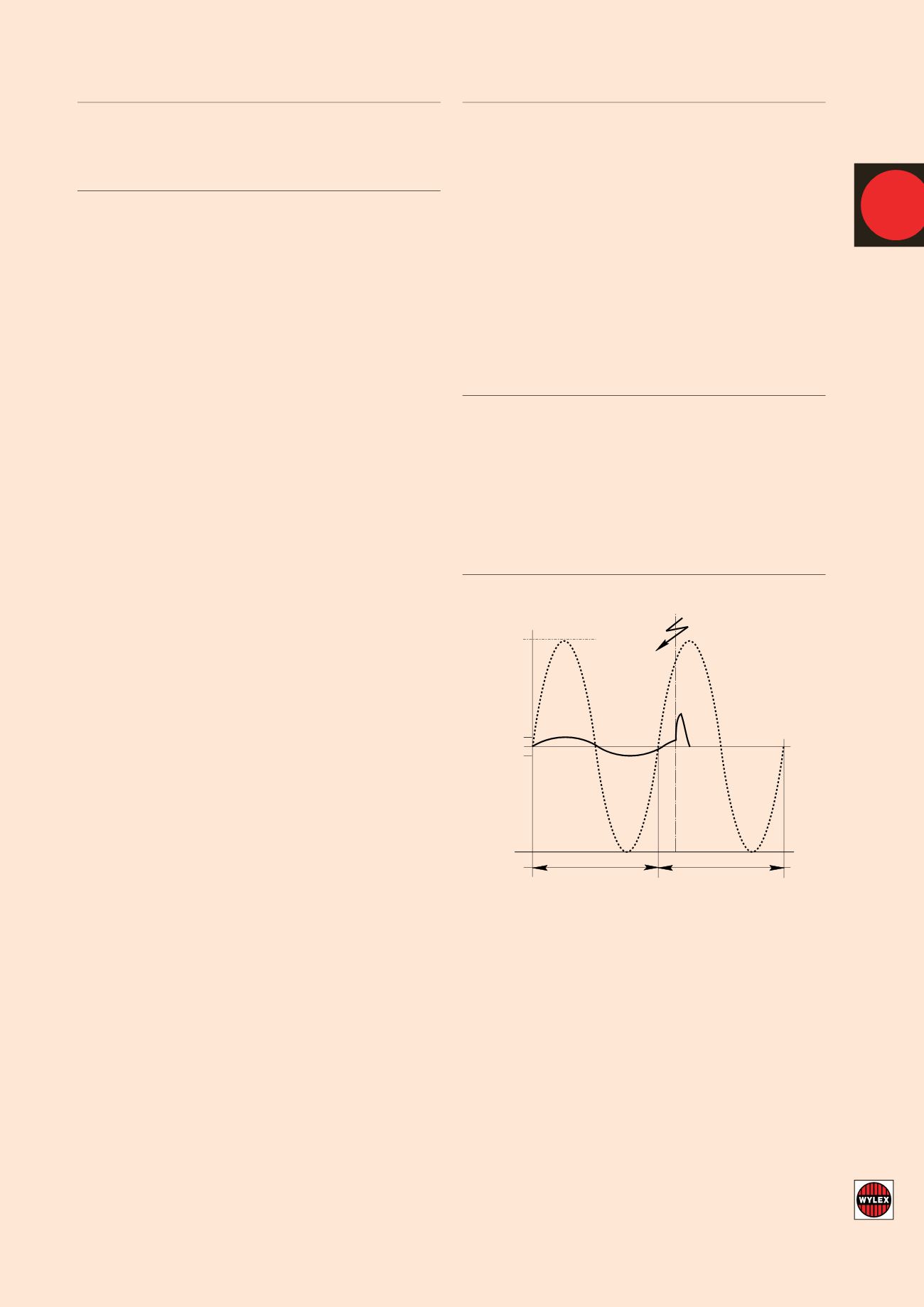
CURRENT LIMITING ACTION
The high speed current limiting action ensures that the MCB operates
before the full prospective fault current is allowed to develop.
Under fault conditions, damage can be sustained to the installation and
associated equipment due to the amount of energy that passes before
the current is completely interrupted.The total energy let-through
depends on the value of current and the time for which it flows, and is
denoted by the symbol I
2
t.The high speed current limiting action of
MCBs ensures that the energy let-through and any subsequent damage
is minimised.This reduced energy let-through assists greatly with both
back-up and discrimination considerations.
CURRENT LIMITING EFFECT
Maximum
prospective
fault
current
Healthy
circuit
current
Fault
20ms
20ms