Total Solution to Earthing & Lightning Protection |
9AKK106354A3360
16/27
16
Instrumentation
Instrument
Earth
ESP SL30X/I
ESP SL30X
Control cabinet
IP54
enclosure
Instrument
Earth
System
Earth
Field
earth
Open end cable screen
ZONE 0
Hazardous Area Zones 1, 2
Non-Hazardous Area
Isolated
coupling
IS
Barrier
ZONE 1
ZONE 2
Lightning protection of hazardous areas
in line with ATEX/IECEx
With hazardous areas at risk from the consequences of
direct and indirect lightning, a comprehensive approach to
lightning protection in line with IEC/BS EN 62305 should
be considered. This should cover structural lightning
protection, earthing and equipotential bonding, and transient
overvoltage protection. The zonal approach to lightning
protection, as established in IEC/BS EN 62305 is applicable
for designing an LPS suitable for hazardous areas,
considering the following points.
Structural lightning protection
For locations with potentially explosive atmospheres, as
defined by IEC/BS EN 62305 the appropriate Class of LPS
required shall be dictated by the risk assessment
process in IEC/BS EN 62305-2.
An isolated LPS is required since the structure includes
combustible materials and/or presents a risk of explosion,
with minimum separation distances adhered to between the LPS
and structural metallic parts to remove any risk of sparking.
Additionally, catenary conductors raised high above the structure
should be considered, where these are to protect locations
where combustibles are present, such as gas/oil storage tanks.
Earthing & equipotential bonding
The earth termination system should meet the requirements
set out in IEC/BS EN 62305-3 a single, integrated earth
termination system combining lightning protection, power and
telecommunications systems. It should provide low electrical
resistance (less than 10 Ohms) and be appropriately
bonded to ensure no metallic part is at a different potential
with respect to another. Where incoming or outgoing services
cannot be bonded directly to earth, these should be
protected by a suitable SPD.
Following the zonal approach in IEC/BS EN 62305, services
passing from LPZ 0 to LPZ 1 should be protected against
partial lightning currents using a lightning current/equipotential
bonding SPD (tested to 10/350 μs waveform), as well as
transient overvoltages (SPD tested to 8/20 μs waveform).
Electronic systems protection
Electrical and electronic equipment/systems need to be
protected against transient overvoltages, since damage to
components could lead to risk of sparks or fire. Equipment/
systems sited in a safe area which do not contribute to safety
in a potentially explosive atmosphere can be protected
against transient overvoltages using appropriate standard
SPDs, as defined by IEC/BS EN 62305.
However, equipment/systems sited in potentially explosive
atmospheres (Zone 1, 2) or contributing to safety within these
atmospheres require an SPD suitably tested and approved by
ATEX. All SPDs installed on site should form a coordinated
set to ensure protection levels are maintained and
effective throughout.
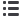
Protection of intrinsically safe (IS) circuits
Intrinsic Safety (IS) is a concept for protecting hazardous areas
from dangerous sparking, whereby sparks from electrical
equipment and circuitry are prevented through the use of IS
barriers. These barriers limit the available electrical energy that
could cause an explosion to below ignition threshold.
IS Barriers however are not surge protectors but are field
instruments which are themselves at risk from transient
overvoltages. IS circuits therefore need to be protected from
transient overvoltages by a suitable (ATEX approved) SPD.
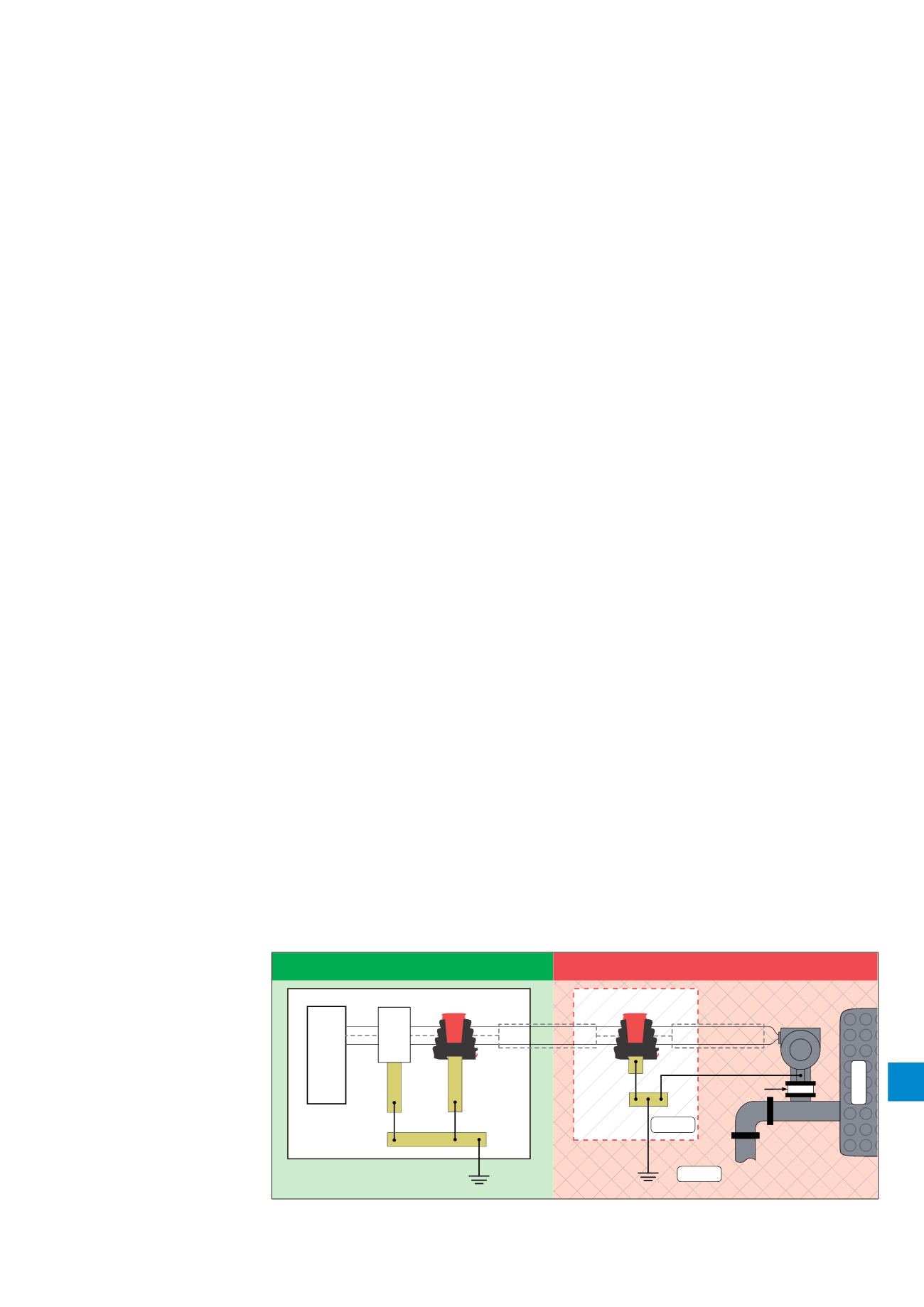
Protection should be applied at the boundary between
the hazardous and non-hazardous area (see Figure 9), with
an isolated screen SPD installed within the hazardous area
(Zone 1, 2).
Figure 15: The installed SPD (here
the ESP SL30X Series) provides
protection for the instrumentation
as well as providing protection for
the IS Barrier. The isolated screen
version (ESP SL30X/I) should be
used in Zone 1, 2.