2/4
Total Solution to Earthing & Lightning Protection |
9AKK106354A3360
2
Introduction to lightning protection
Product selection guide
Conductors
The first choice faced by the designer of a structural lightning
protection system is the type of conductor system to be used:
–– Choose the material required, i.e. copper or aluminium
–– Choose the type of conductor required, i.e. flat tape, solid
circular or stranded
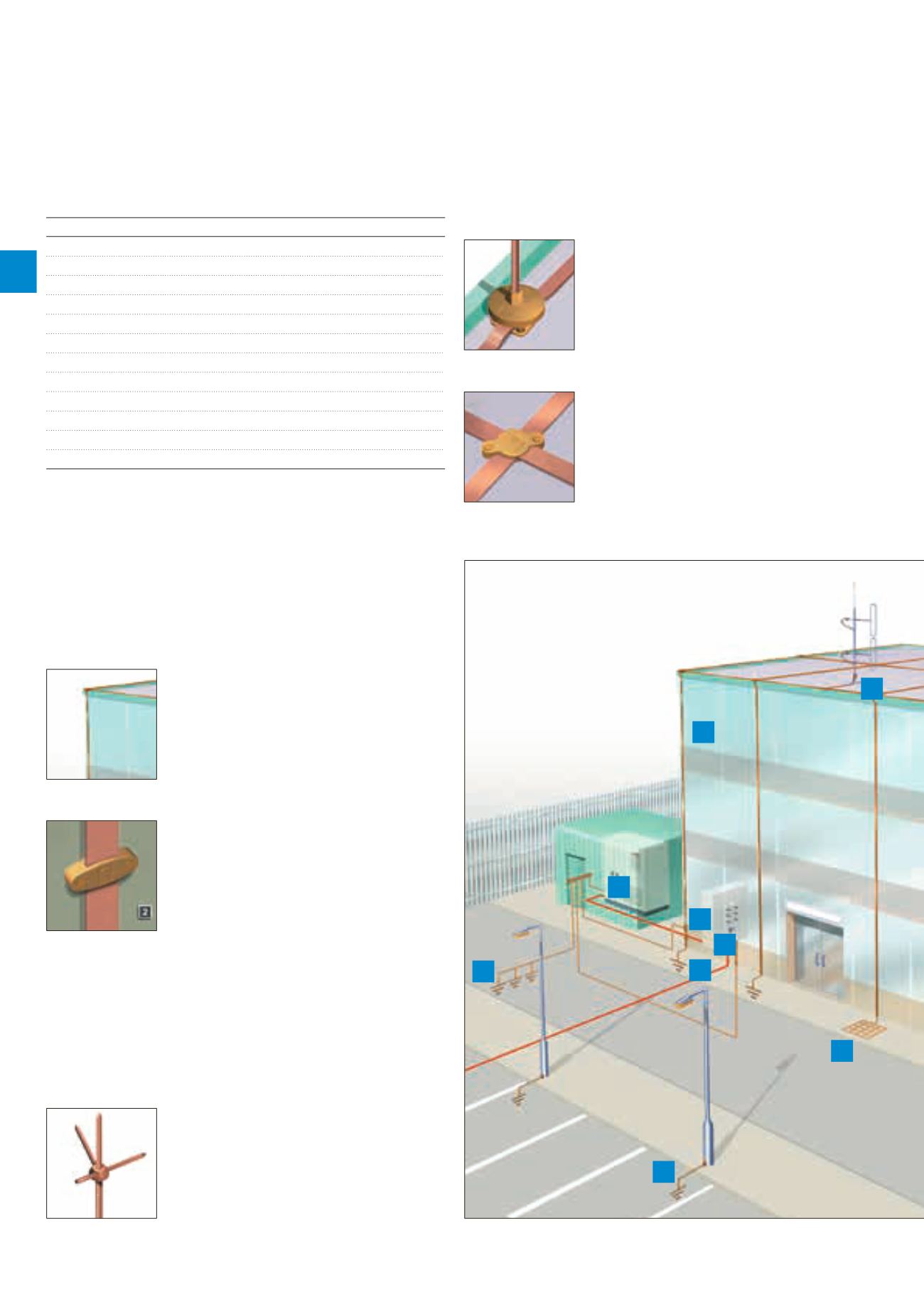
1. Conductor network
The conductor network is the means of
intercepting/carrying the current of a
lightning strike safely to the earth
termination network. Use the guidelines
of IEC/BS EN 62305-1 & -3 for the
correct placement of conductors.
2. Fixings
Select the correct system of fixings for
each part of the conductor system.
Fixings are available for a wide range of
modern construction materials,
e.g. brick, stone, plastic and metal.
Air termination network
The air termination network is the point of connection for a
lightning strike. It typically consists of a meshed conductor
arrangement covering the roof of the structure. The mesh size
is determined by Lightning Protection Level - LPL.
3. Air terminals
Use air terminals in the form of vertical air
rods for the protection of prominent
roof top features or equipment. Use strike
pads to connect and thus expose
concealed conductors.
Air termination network
4. Air rod bases
Choose the correct air rod base. This
will ensure that the vertical air rods
are both solidly fixed to the fabric of the
structure and have a low resistance
connection to the conductor network.
5. Interconnection components
Crossover clamps have been specially
designed for use where conductors cross
as part of a roof network.
Main aspects and individual components of an external lightning protection system
5
8
12
1
8
8
8
12
11
1
2
3
4
5
Product selection guide - Lightning protection
No.
Type
Section
/ Page No.
1.
Conductors
3/4
2.
Conductor fixings
5/2
3.
Air terminals
4/3
4.
Air rod bases
4/4, 4/11
5.
Conductor jointing clamps
5/16
6.
Test clamps
5/19
7.
Crossover conductor clamp
5/16
8.
Earth electrodes
7/3, 7/10
9.
Earth rod clamps
8/2
10.
Earth inspection pits
7/9
11.
Bonds
8/10
12.
Lightning current or equipotential bonding SPDs 11/3