11
11/36
Dimensions
Section 12
Typical applications
Direct current has been used for a long time and in many fields. It offers major
advantages, in particular immunity to electrical interference. Moreover, direct-current
installations are now simpler, because they benefit from the development of power
supplies with electronic converters and batteries.
b
b
Communication or measurement network:
v
v
48 V DC switched telephone network,
v
v
4-20 mA current loop.
b
b
Electrical supply for industrial PLCs:
v
v
PLCs and peripheral devices (24 or 48 V DC).
b
b
Auxiliary uninterruptible direct current power supply:
v
v
relays or electronic protection units for MV cubicles,
v
v
switchgear opening / closing trip units,
v
v
LV control and monitoring relays,
v
v
indicator lights,
v
v
circuit-breaker or on/off switch motor drives,
v
v
power contactor coils,
v
v
control/monitoring and supervision devices with communication that can be
powered via a separate uninterruptible power supply.
b
b
24 to 48 V DC wind application:
v
v
isolated homes,
v
v
cottages, bungalows, mountain refuges,
v
v
pumps, street lighting,
v
v
measuring instruments, data acquisition,
v
v
telecommunication relays,
v
v
industrial applications.
Types of direct current networks
According to the types of DC networks illustrated below, we can identify the risks to
the installation and define the best means of protection.
For further information on the types of networks and the faults that characterise them, refer to
the direct current circuit breaker (LV) selection guide, 220E2100.indd.
For all these configurations, we propose a single protection solution that depends
only on the requirement for the nominal current In and the short-circuit current Isc at
the installation point concerned.
The second important point in our solution is the fact that the protection is
implemented by non-polarised circuit breakers that can operate efficiently,
whatever the direction of the direct current.
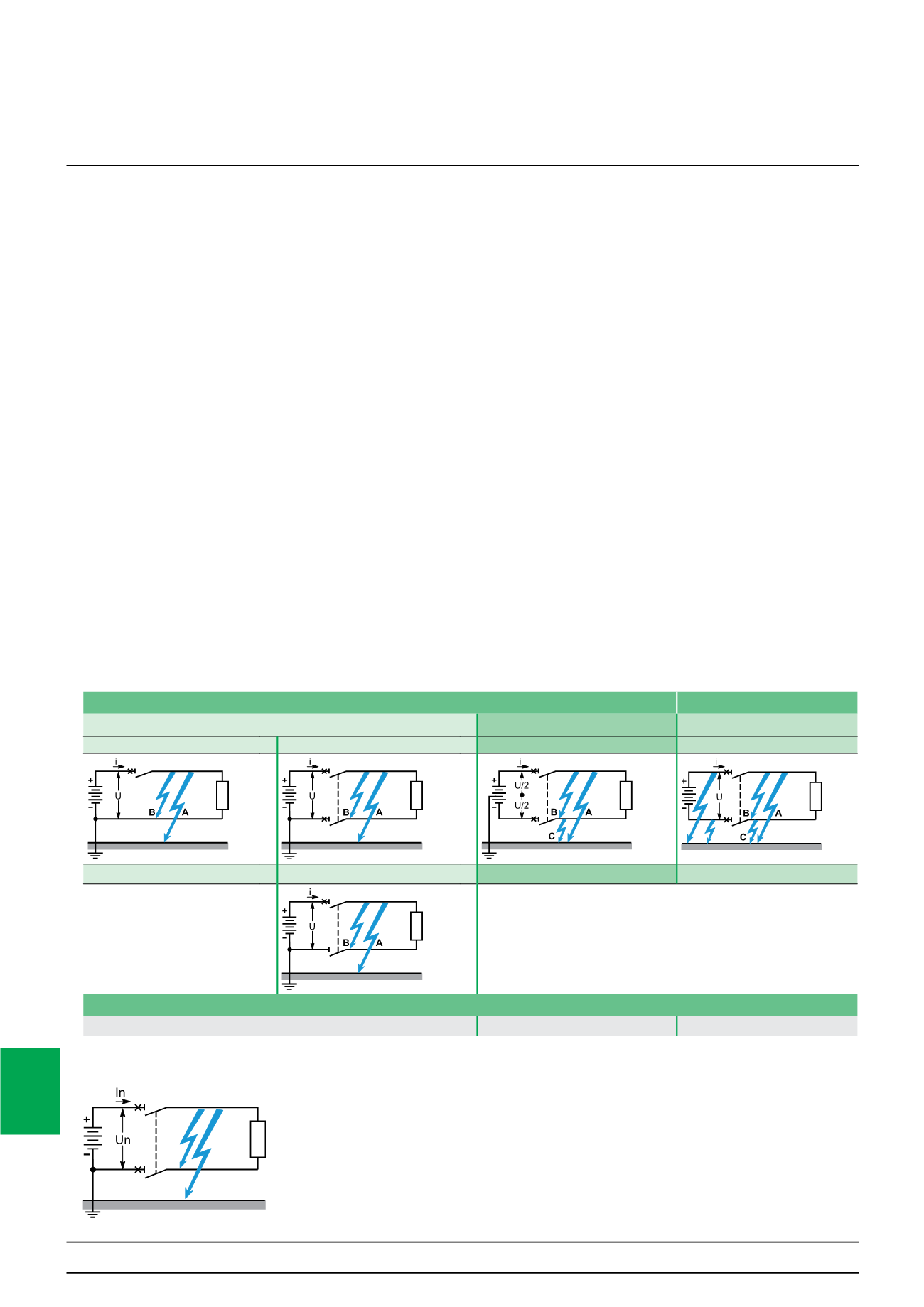
DB124236
Earthed
Isolated from earth
I
: Earthed (or grounded) polarity (in this case negative)
II
: Earthed mid-point
III
: Isolated polarities
1 pole (1P isolation)
2 poles (2P isolation)
2 poles
2 poles
DB124075
DB124067
DB124076
DB124068
D
E
2 poles (1P isolation 1P+N)
DB124387
Worst-case faults
Fault A and fault B (if only one polarity is protected)
Fault B
Double fault A and D or C and E
Isc
Circuit breakers for direct
current applications
24 V - 48 V direct current applications
Technical advice