Total Solution to Earthing & Lightning Protection |
9AKK106354A3360
10/5
10
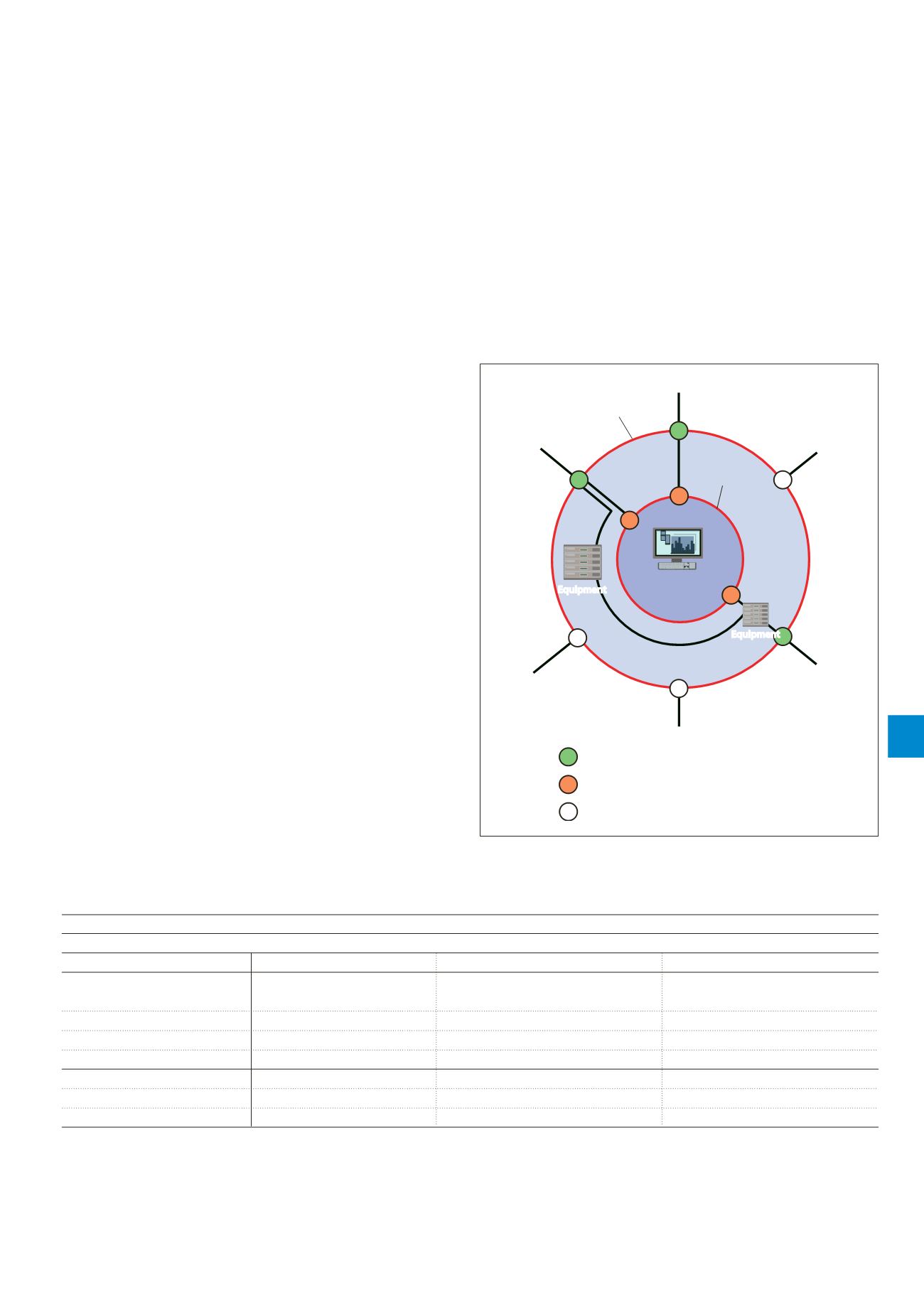
A series of zones is created within the structure according to
the level of threat posed by the LEMP with each zone to have
successively less exposure to the effects of lightning - for
example LPZ 0 (outside the structure) where the threat of
lightning currents and fields is most severe being more
onerous than LPZ 3 (within the structure) where the threat of
lightning is considerably reduced such that electronics can be
safely located within this zone.
Figure 1. illustrates the basic LPZ concept defined by
protection measures against LEMP as detailed in
IEC/ BS EN 62305-4. Equipment is protected against both
direct and indirect lightning strikes to the structure and
connected services, through the use of Surge Protection
Measures (SPM), formerly referred to as a LEMP Protection
Measures System (LPMS).
To achieve this reduction in LEMP severity, from conducted
surge currents and transient overvoltages, as well as radiated
magnetic field effects, successive zones use a combination
of shielding measures, bonding of incoming metallic services
such as water and gas and the use of coordinated SPDs
(further details can be found in the Furse Guide to
BS EN 62305 Protection Against Lightning).
Given that the live cores of metallic electrical services such as
mains power, data and telecom cables cannot be bonded
directly to earth wherever a line penetrates each LPZ, a
suitable SPD is therefore needed.
The SPDs characteristics at the boundary of each given zone
or installation location need to take account of the surge
energy they are to be subject to as well as ensure the
transient overvoltages are limited to safe levels for equipment
within the respective zone.
Table 1, below, details the standardized test waveforms with
peak currents used to test SPDs typically located at each
zone boundary.
Table 1:
Standardized test waveforms with peak currents used to test SPDs at each LPZ boundary
SPD location/LPZ boundary
LPZ 0/1
LPZ 1/2
LPZ 2/3
Typical SPD installation point
Service Entrance (e.g. Main distribution Sub-distribution board or telecom
Terminal Equipment (e.g. socket outlet)
board or telecom NTP)
PBX frame
Mains Test Class/SPD Type
(1)
I/1
II/2
III/3
Surge test waveform
10/350 current
8/20 current
Combination 8/20 current and 1.2/50 voltage
Typical peak test current (per mode)
25 kA
(2)
40 kA
3 kA (with 6 kV)
Signal/Telecom Test Category
(1)
D1
(3)
C2
(3)
C1
Surge test waveform
10/350 current
Combination 8/20 current and 1.2/50 voltage Combination 8/20 current and 1.2/50 voltage
Typical peak test current (per mode)
2.5 kA
2 kA (with 4 kV)
0.5 kA (with 1 kV)
(1)
Tests to BS EN 61643 series
(2)
Peak current (per mode) for a 3 phase SPD to protect a TN-S mains system
(3)
Test category B2 10/700 voltage waveform (also within ITU-T standards) up to 4 kV peak
also permissible
Boundary
of LPZ 2
(shielded room)
Boundary
of LPZ 1
(LPS)
Antenna
Electrical
power line
Water pipe
Gas pipe
Telecoms
line
Mast or
railing
LPZ 2
B
B
B
B
LPZ 1
Critical
equipment
Equipment
SPD 1/2 - Overvoltage protection
Connected service directly bonded
SPD 0/1 - Lightning current protection
Equipment
LPZ
0
FIgure 1. Basic LPZ concept - IEC/ BS EN 62305-4